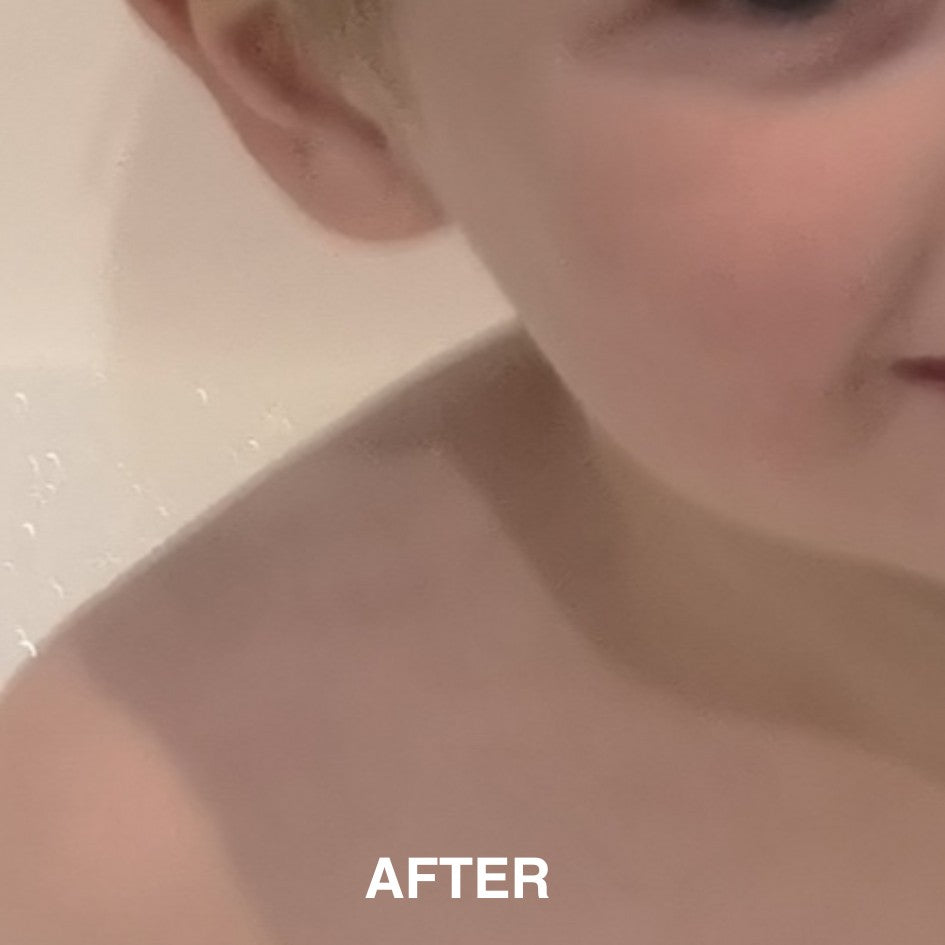
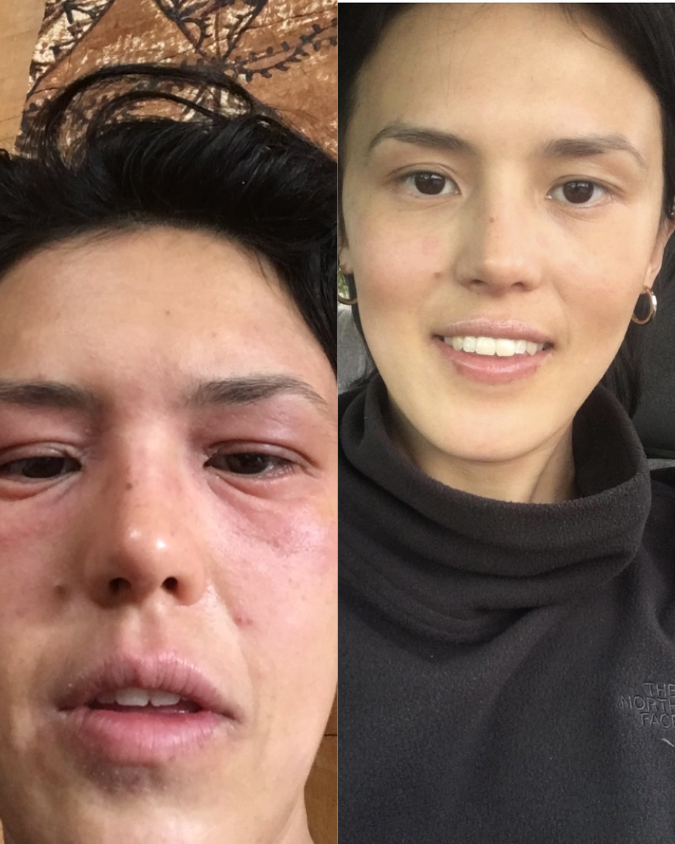
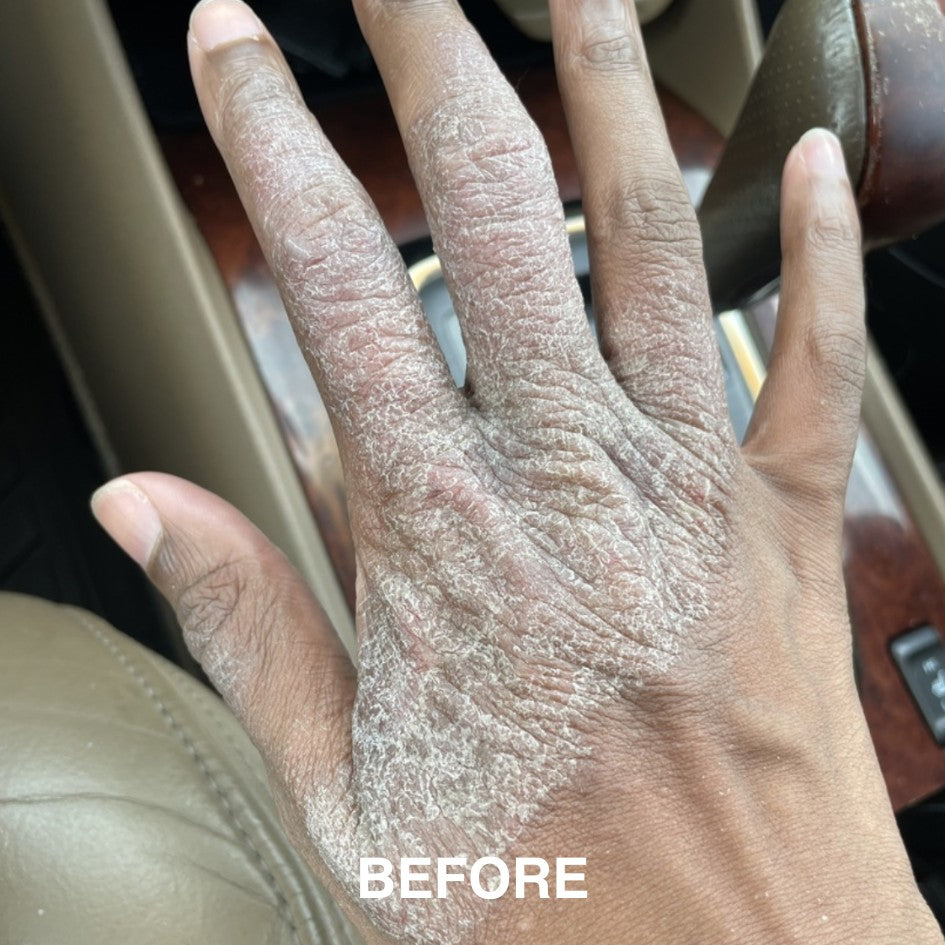
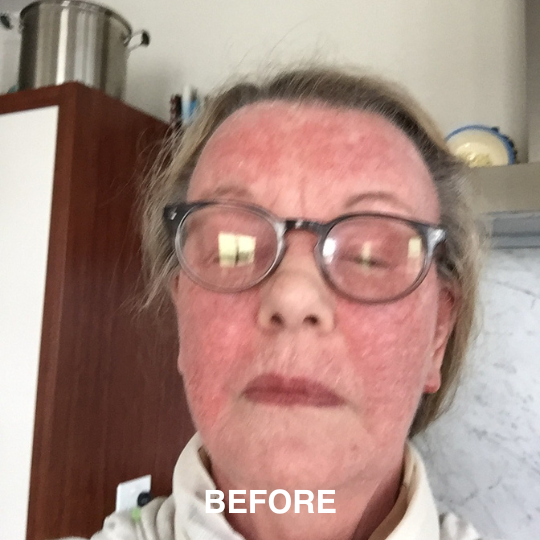
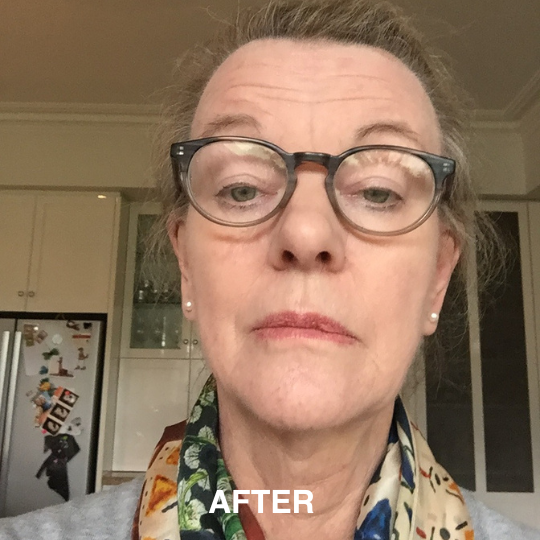
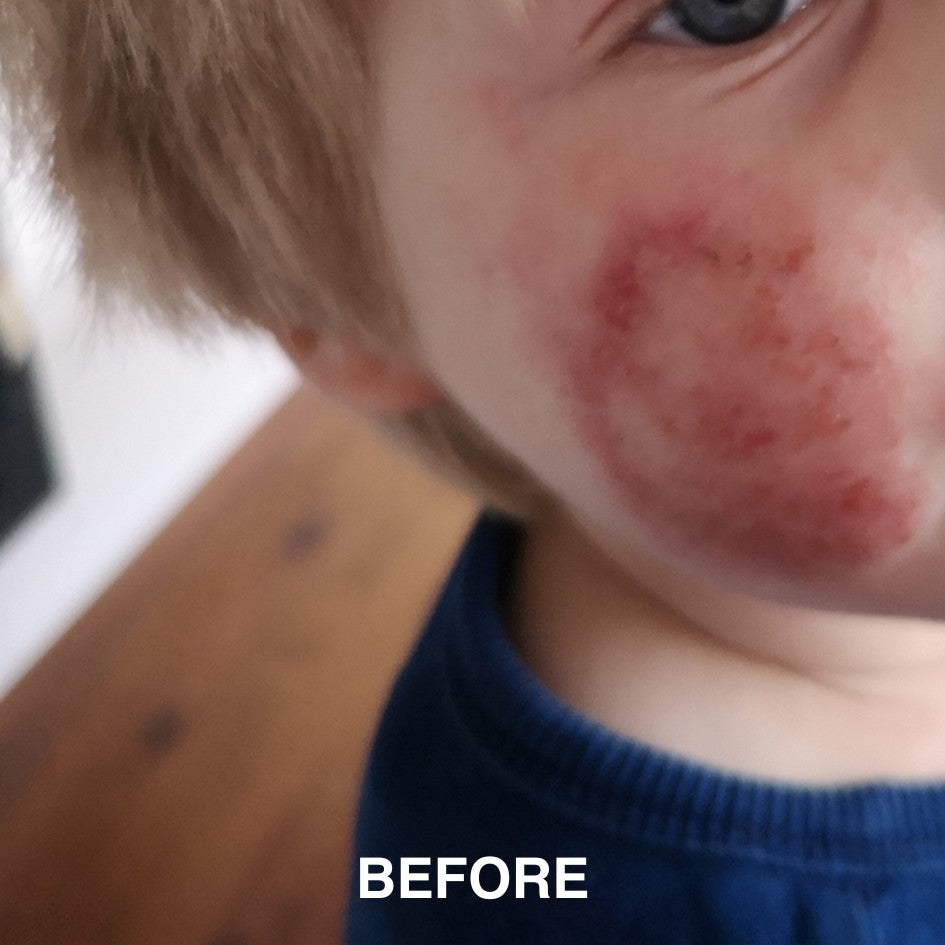
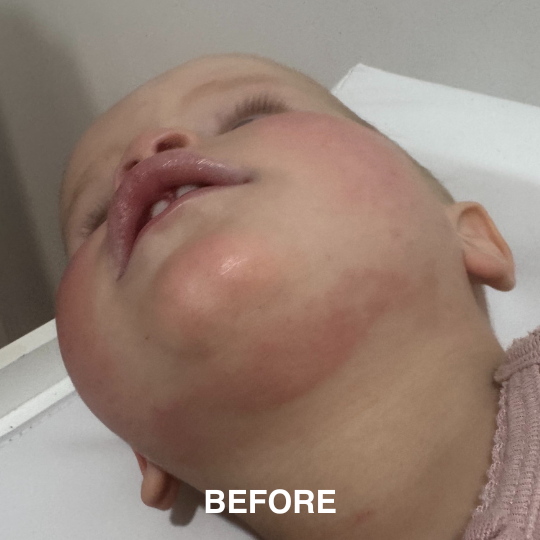
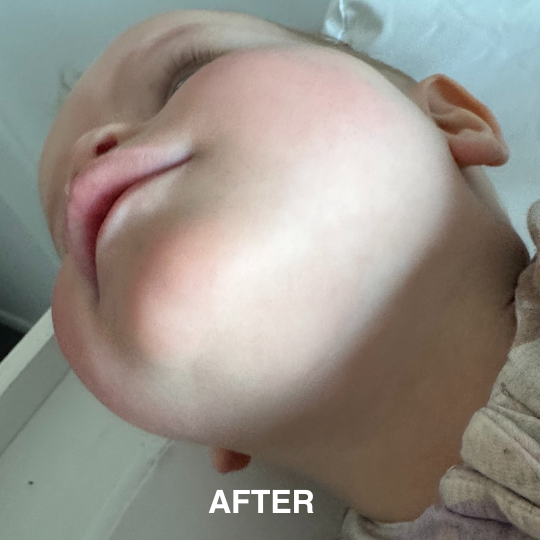
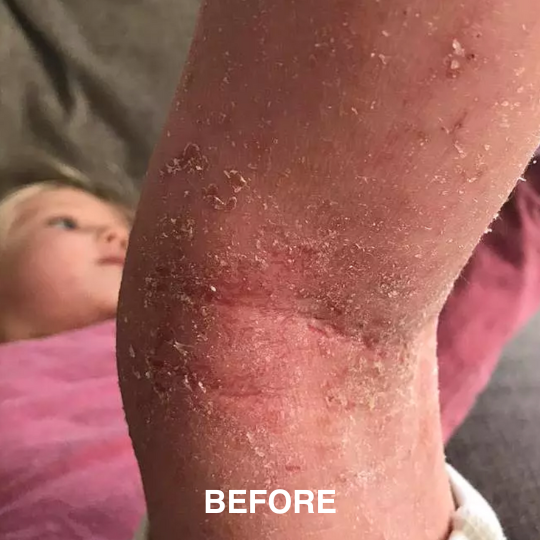
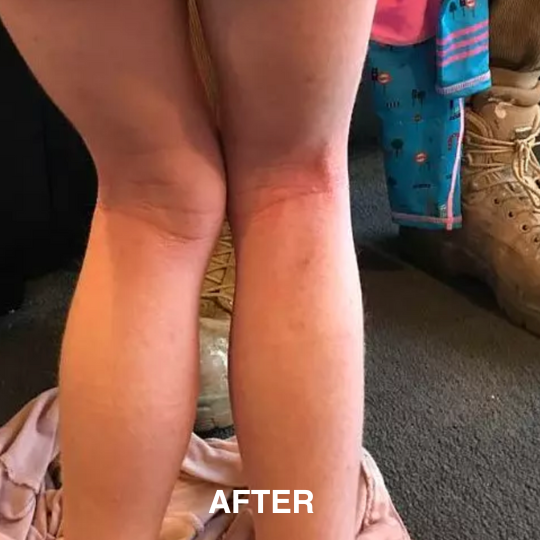
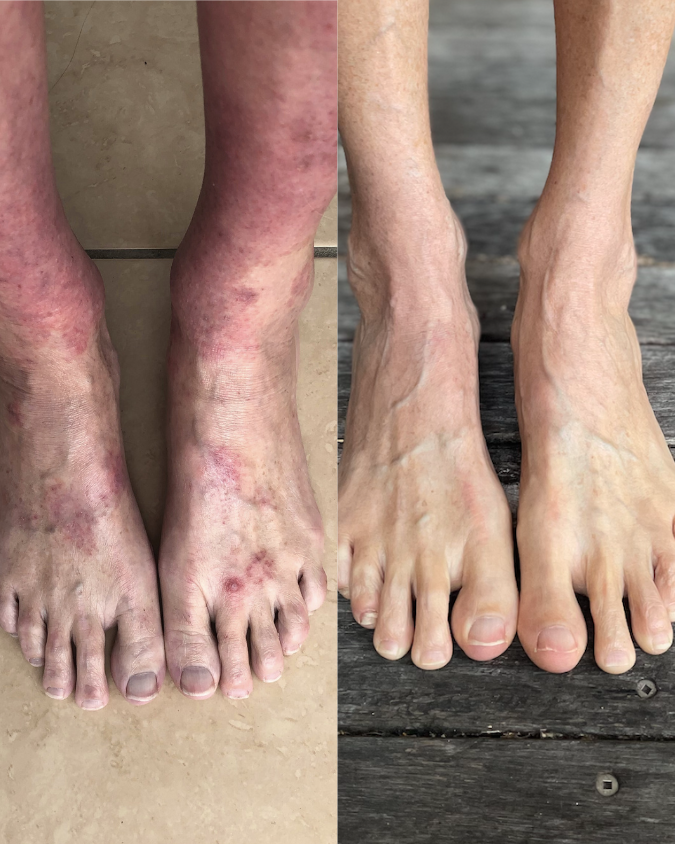
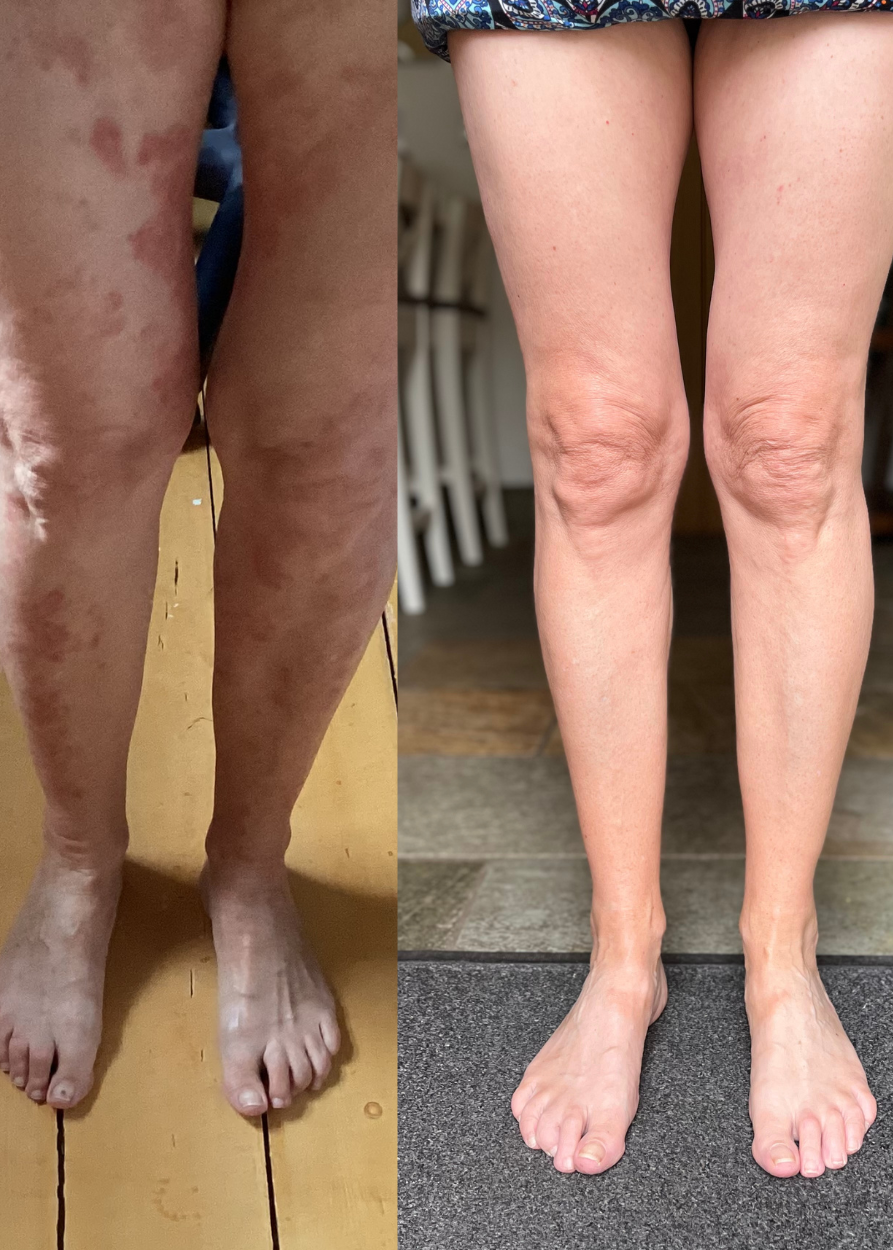
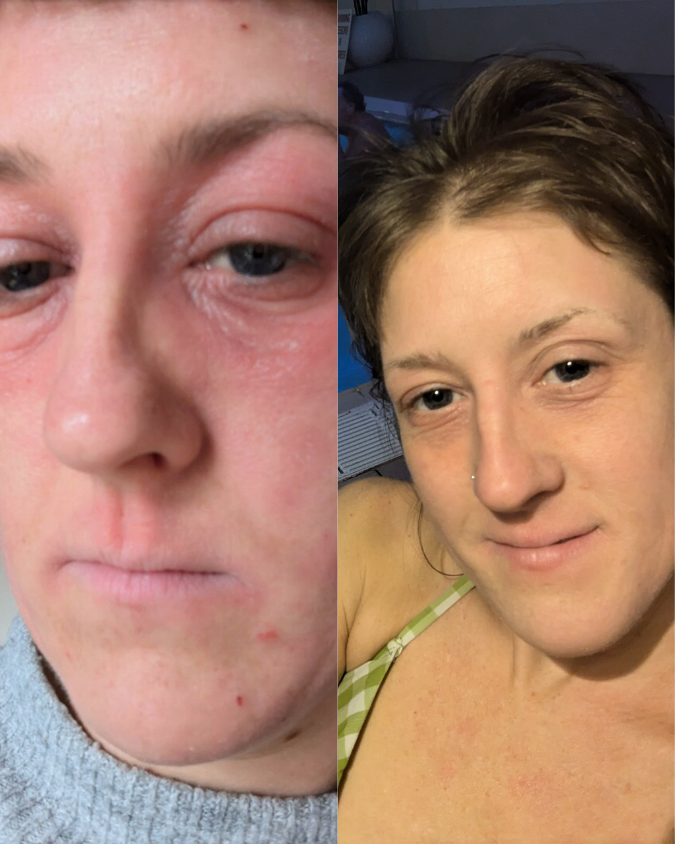
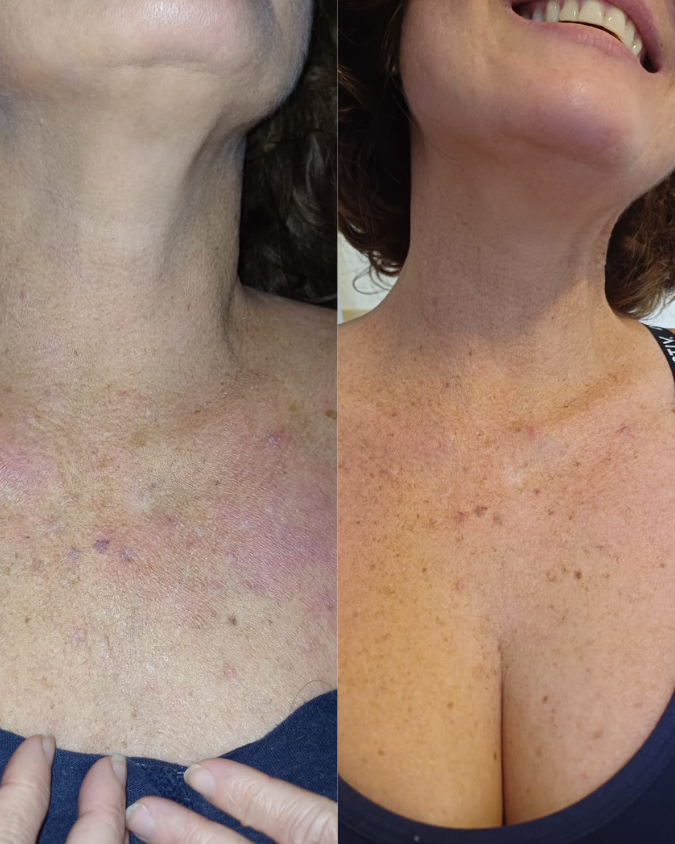
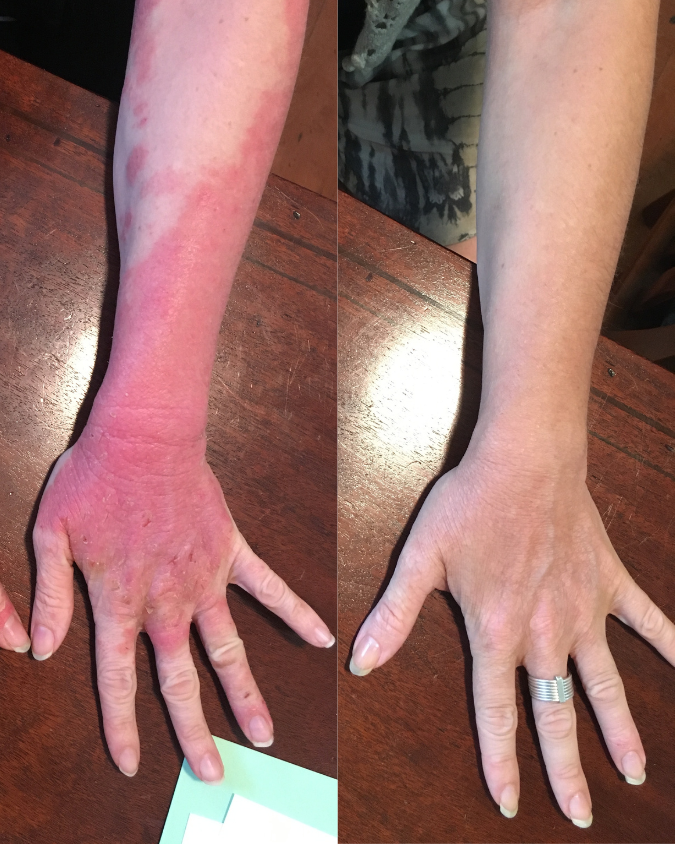
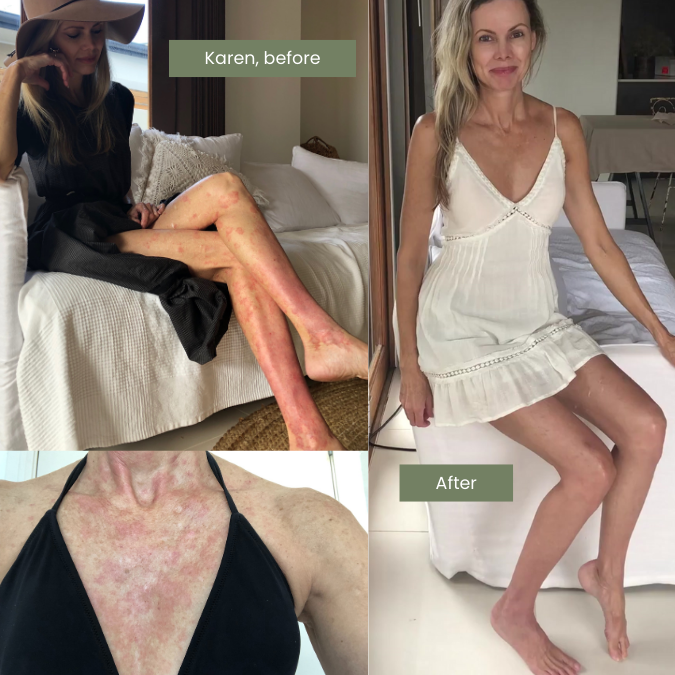
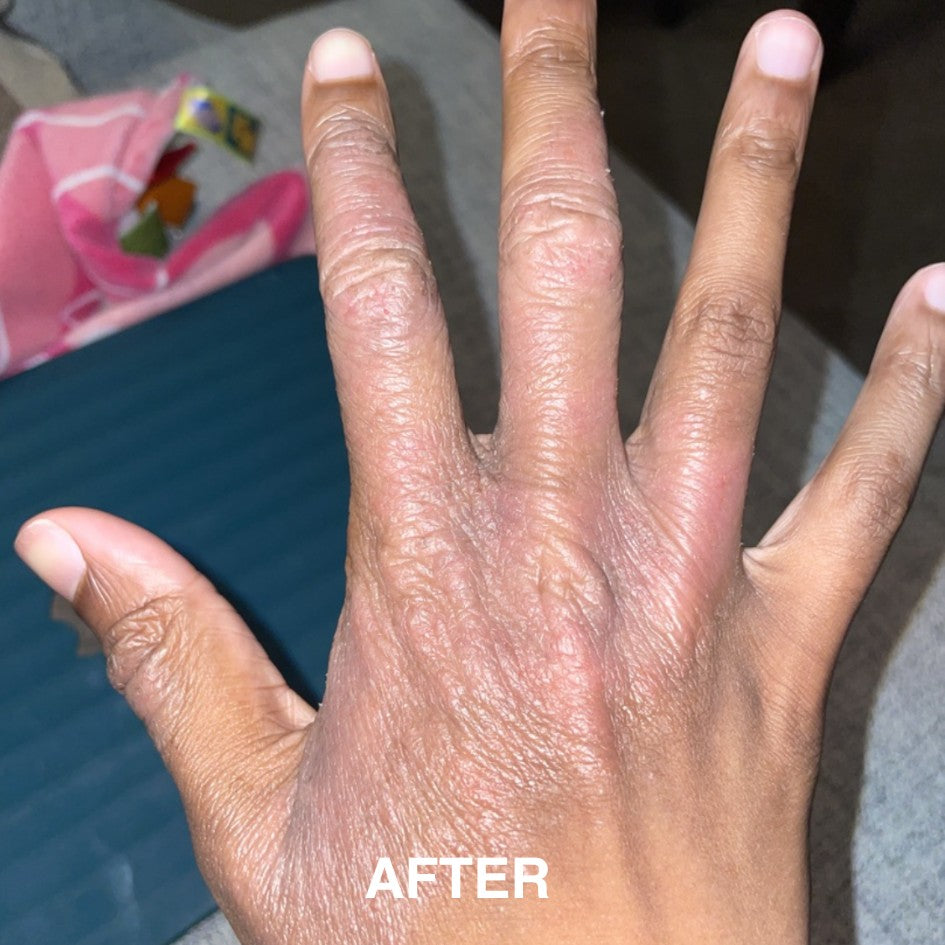
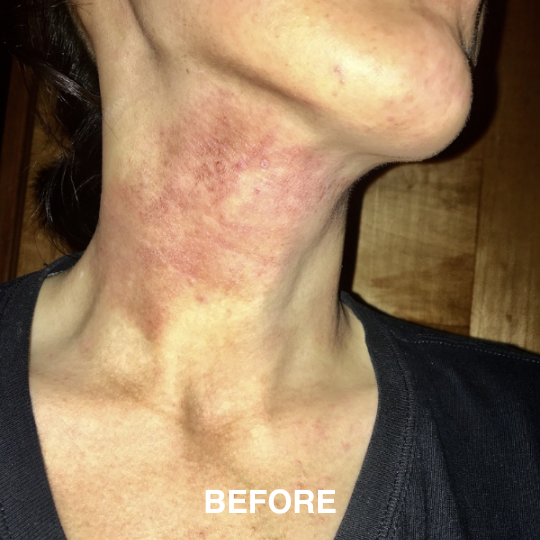
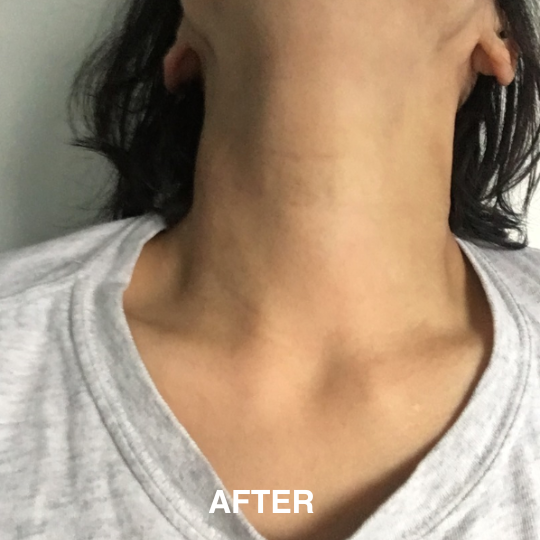
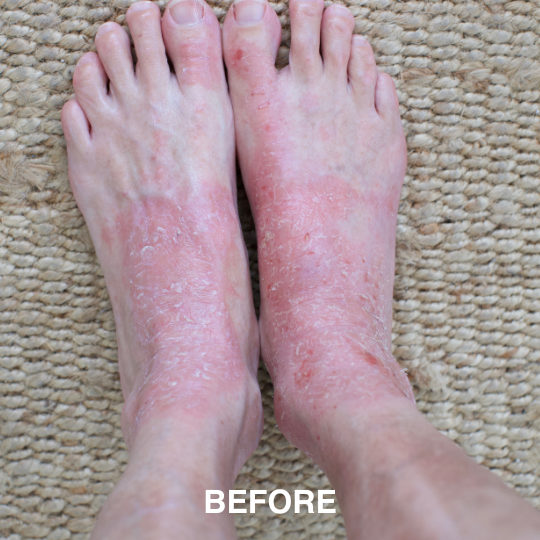
If you’re managing eczema, you’ve likely tried countless creams and treatments.
But did you know that the health of your gut could be playing a role in your skin condition? The link between poor digestion and skin problems is well-documented, with eczema studies showing that an imbalanced gut microbiota is linked to increased inflammation and eczema (also known as atopic dermatitis).
Let’s explore this connection and how you can support your gut for clearer, healthier skin.
The Gut-Skin Connection: Why It Matters
Your gut does more than just digest food. It’s a key player in regulating your immune system, managing inflammation, detoxification and delivering nutrients (Wu, 2012)—all of which directly affect your skin. When your gut health is compromised, it can show up as leaky gut and skin disorders, including eczema and other inflammatory conditions.
What Is Leaky Gut and Does It Create Skin Disorders?
Leaky gut happens when the gut lining becomes damaged, allowing toxins, bacteria, and undigested food particles to escape into your bloodstream (Camilleri, 2019). This triggers an immune response, which can cause widespread inflammation. For eczema sufferers, this can mean more frequent and intense flare-ups.
The gut and skin are linked in several ways:
- Inflammation from Gut Damage: Toxins that escape the gut can exacerbate eczema symptoms by triggering an overactive immune response.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Nutrient deficiencies including zinc deficiency and vitamin K2, which are essential for gut repair and gut microbiome protection, can lead to leaky gut symptoms
- Weakened Immune System: Your gut houses a large portion of your immune system. When the gut is unbalanced, it can leave your skin more vulnerable to irritation.
The Role of Zinc in Gut and Skin Health
When you’re trying to overcome poor digestion and skin problems, zinc is a crucial mineral. Zinc deficiency is linked to inflammation of the gut, and research shows that zinc can help repair the gut wall, reducing the likelihood of toxins escaping into the bloodstream. This mineral also supports skin healing, making it a key player in addressing leaky gut and skin disorders like eczema.
The Skin Friend AM Activated Multi includes an active dose of zinc (15 mg for adults), along with other essential nutrients, to assist in the repair of the gut wall lining and reduce inflammation from within.
Probiotics for Eczema
While probiotics were once touted as a new treatment for eczema, researchers are now unsure if they really help this skin condition. What's worse, the long-term safety of probiotics is now in doubt.
According to a well-researched Cochrane Review, there is currently no scientific evidence that probiotics can relieve eczema (
Makrgeorgou, 2018). What’s worse there is some evidence that probiotics can cause infections and gut damage. The researchers concluded "Current use of probiotics for treatment of eczema is not evidence‐based" and some studies found probiotic use could lead to sepsis (a life threatening infection!) and bowel ischaemia, which is a reduction in blood flow to the gut, resulting in pain.
So while uncommon, long-term use of probiotics may lead to harmful side-effects in some people.
Probiotic use can also trigger inflammation in the body and increase the number of bacteria that cause gut inflammation. An increase in the risk of heart disease was also found after extended use of probiotics (Hradicka, 2023).
In light of the new evidence, I no longer recommend probiotics for eczema.
FAQ: I need to take antibiotics for my skin infection, so what can I take to protect my gut during antibiotic use?
Protecting Your Gut During Antibiotic Use
Antibiotics are sometimes necessary for infected eczema, but they can disrupt the delicate balance of gut bacteria. So instead of reaching for a probiotic after your microbiome has been damaged, try vitamin K2. Studies show that vitamin K2 (specifically the menaquinone 7 form) can PROTECT your gut microbiome during antibiotic treatment, reducing the risk of long-term damage. While K2 gut health research is still in the early stages, the results are promising.
The Skin Friend PM Mineral Matrix supplement contains double-encapsulated vitamin K2, making it an excellent choice for maintaining gut health, especially during or after antibiotics.

Image: The Skin Friend PM supplement is a pure powder that contains vitamin K2.
Supporting Gut Health for Clearer Skin
A healthy gut is key to managing eczema and improving skin problems associated with poor digestion. Here are some steps to support your gut health:
1. Add Gut-Supportive Supplements
Supplements can help heal and strengthen the gut lining while providing nutrients for skin health. Skin Friend’s PM Mineral Matrix contains vitamin K2 to protect the microbiome, while the AM Activated Multi includes a therapeutic dose of zinc to support and assist gut wall repair.
2. Eat a Gut-Friendly Diet
Another way to change your gut microbiome is to change your diet. Focus on anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric, red cabbage, fatty fish, and blueberries, such as the diet found in The Eczema Detox book by nutritionist Karen Fischer. Avoid processed foods and common allergens that can irritate the gut lining. Check out the Eczema Detox Clear Skin Toolkit for both a diet and supplement routine for total gut microbiome wellness.
3. Stay Hydrated
Hydration is critical for supporting digestion and flushing out toxins. Adults should aim to consume 2 litres of water daily.
4. Manage Stress
Stress can negatively impact gut health, leading to more inflammation. Practices like yoga, meditation, or short walks can help regulate stress levels.
Heal Your Gut, Heal Your Skin
How gut health affects the skin is clear: a healthy gut supports clearer, calmer skin. You can reduce flare-ups and promote lasting skin health by assisting the gut lining repair process, balancing your microbiome, and supplementing with nutrients like zinc and vitamin K2.
Start your journey today with Skin Friend’s gut health products. A healthier gut means healthier skin—inside and out. Click the image to find out about our complete gut and skin health program: The Eczema Detox Clear Skin Toolkit.

Click for references
Aldars-García L, Chaparro M, Gisbert JP. (2021). Systematic Review: The Gut Microbiome and Its Potential Clinical Application in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Microorganisms. 9(5):977. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33946482/. PMID: 33946482; PMCID: PMC8147118.
Díez-Madueño K, et al. (2025). Gut Dysbiosis and Adult Atopic Dermatitis: A Systematic Review. J Clin Med. 14(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010019.
Wu HJ, Wu E. (2012). The role of gut microbiota in immune homeostasis and autoimmunity. Gut Microbes. 3(1):4-14. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3337124/. PMID: 22356853; PMCID: PMC3337124.
Camilleri M. (2019). Leaky gut: mechanisms, measurement and clinical implications in humans. Gut. 68(8):1516-1526. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31076401/. PMID: 31076401; PMCID: PMC6790068.
Zupo R, et al. (2022). Prevalence of Zinc Deficiency in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 14(19):4052. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36235709/. PMID: 36235709; PMCID: PMC9572015.
Lin PH, et al. (2017). Zinc in Wound Healing Modulation. Nutrients. 10(1):16. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29295546/. PMID: 29295546; PMCID: PMC5793244.
Makrgeorgou A, et al. (2018). Probiotics for treating eczema. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 11(11):CD006135. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006135.pub3. PMID: 30480774; PMCID: PMC6517242.
Hradicka P, et al. (2023). Addressing safety concerns of long-term probiotic use: In vivo evidence from a rat model. J Funct Foods. 104:105521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2023.105521.